Publications
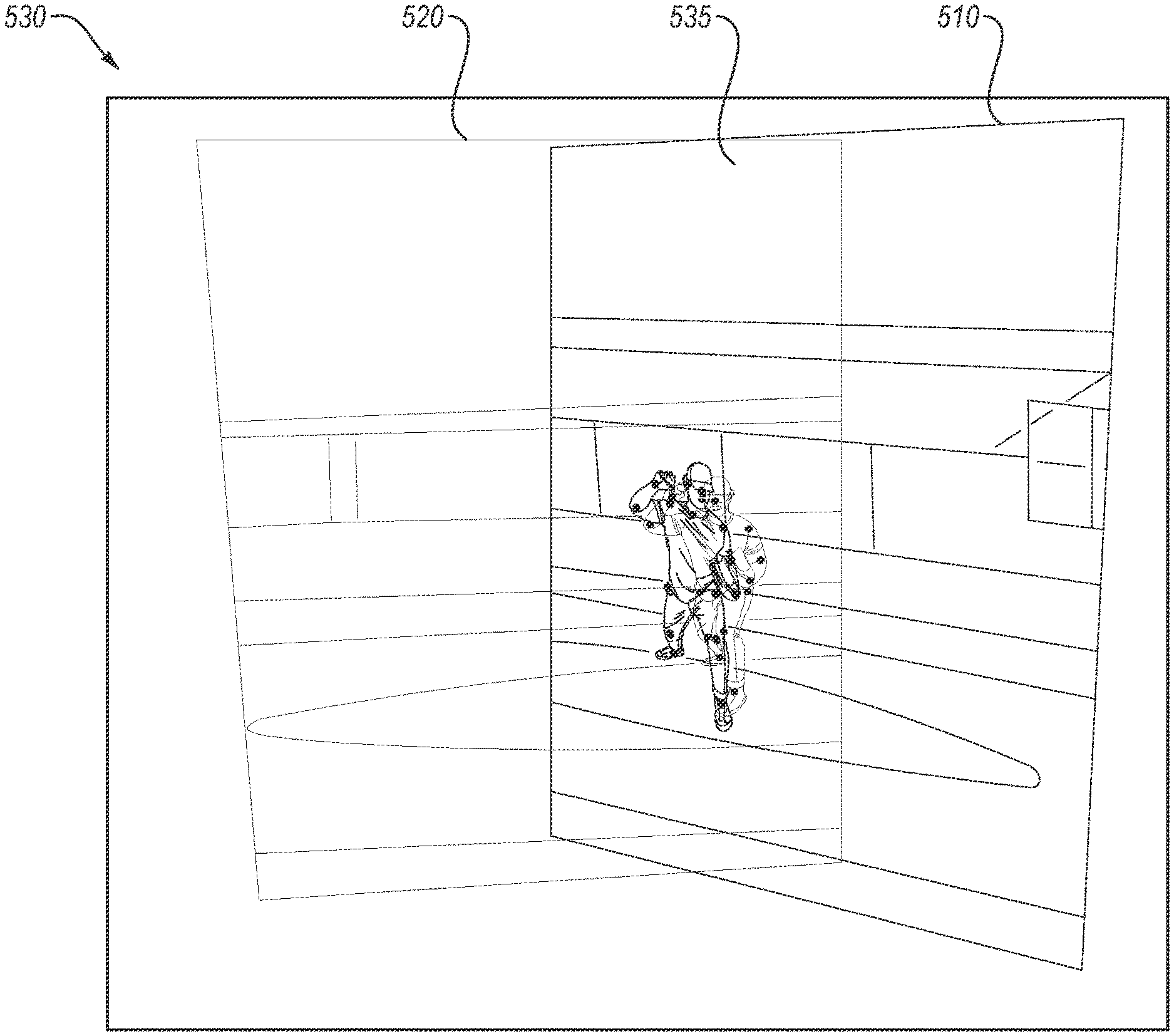
This method describes an innovative way to accurately analyze an object's motion (like a person or a ball) when it's tracked by multiple video cameras.
Key Steps in the Method:
- Capture Data: Collect video (image data) of the object's motion simultaneously from at least two separate cameras.
- 2D Pose Estimation: For each frame, identify the object and determine the 2D position of its key features.
- 3D Heatmap Generation: Create 3D joint heatmaps for the object in each camera's view.
- Determine Time Delay: Compare these 3D heatmaps to pinpoint the exact time lag or delay between cameras.
- Generate Motion Journal: Synchronize the video feeds and generate a complete motion journal summarizing the object's movement over time.
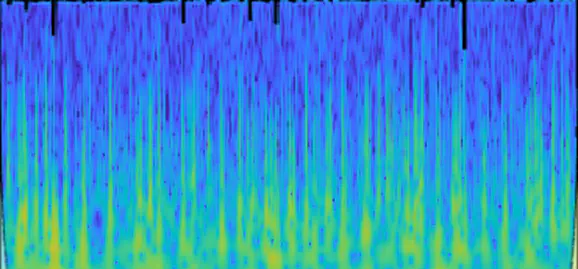
The study aimed to classify task difficulties using wavelet transform images of EEG signals and deep learning models. The EfficientNet-B0 model achieved the highest accuracy, but its performance varied significantly across individuals and task difficulties, indicating limited generalizability. The study suggests a need for further research to improve model generalizability, optimize performance, and validate the models on larger, more diverse datasets.
Electroencephalogram (EEG) signals provide a non-invasive method to study cognitive processes. This study aimed to classify Multi-Attribute Task Battery (MATB) task difficulties based on wavelet transform images of EEG signals using deep learning models. An EEG dataset collected from 29 subjects while performing the MATB tasks of varying difficulties by Hinss et al. (2023) were transformed into wavelet images that can accommodate time-frequency information at the same time for further analysis. Three deep learning models, EfficientNet-B0, ResNet18, and ResNet50, were trained and tested on these images under different conditions, including pretrained and non-pretrained models, and using different optimizers. The models’ performance was evaluated based on overall accuracy and accuracy by subject, EEG region, and task difficulty. The pretrained EfficientNet-B0 model achieved the highest overall accuracy (77.56%). However, the performance varied significantly across subjects and task difficulties, indicating limited generalizability. The model’s accuracy was lower for medium tasks, suggesting difficulty in distinguishing between medium and other levels of difficulty. While deep learning models can achieve high accuracy in classifying MATB task difficulty based on EEG signals, their performance varies across individuals and task difficulties. Further research is needed to improve model generalizability, optimize performance across all task difficulties, and validate the models on larger and more diverse datasets.